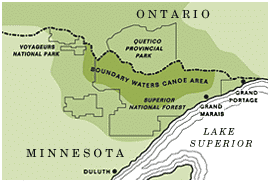
MN DNR protects 16,000 acres in historic northern Minnesota land acquisition
Minnesota DNR recently made history by acquiring one of its largest land holdings. The purchase protects thousands of acres of forested land across multiple counties, in partnership with The Conservation Fund, Northern Waters Land Trust, and ten counties.